YOUR WEBSITE MAY BE FLAGGED BY GOOGLE
Don’t have an SSL Certificate?
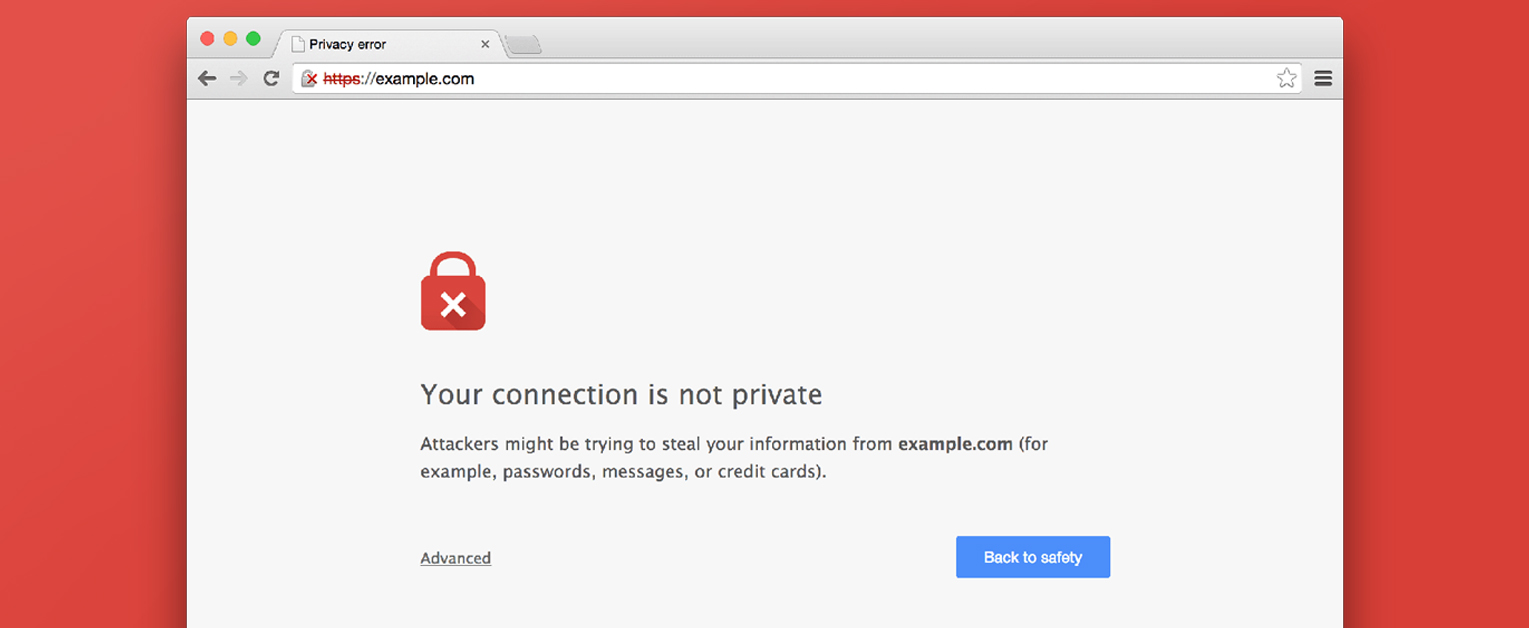
Google is going to flag your website as not secure!
Google is amending their strategy for an even more secure web, as you may have already been aware, Google has been heavily favouring HTTPS (aka the secure version of HTTP) since 2014.
In October 2017, Google started implementing even more changes to prompt all website owners to migrate their websites to HTTPS.
Due to Google’s updated approach, Google’s browser “Chrome” will label your non-HTTPS (HTTP) web pages as “Not Secure” on a number of common circumstances.
Failure to move to HTTPS can result in a significant loss of website rankings, traffic, or visitor trust.
According to Google, it is not advisable to “wait to get started moving to HTTPS”
As they have already announced their intent to mark ALL non-HTTPS pages as “Not Secure” in the very near future.
In short: since October 2017, the Google Chrome browser will show a “Not Secure” warning on:
-
non-HTTPS pages that allow visitor to enter any data
(eg. search bar, contact forms, etc.) -
any non-HTTPS page visited in Incognito Mode
-
non-HTTPS pages that have password fields
(already implemented since January 2017) -
non-HTTPS pages with credit card fields
(already implemented since January 2017)
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is an internet communication protocol that protects the integrity and confidentiality of data between the user’s computer and the site.
Users expect a secure and private online experience when using a website. We encourage you to adopt HTTPS in order to protect your users’ connections to your website, regardless of the content on the site.
Data sent using HTTPS is secured via Transport Layer Security protocol (TLS), which provides three key layers of protection:
- Encryption—encrypting the exchanged data to keep it secure from eavesdroppers. That means that while the user is browsing a website, nobody can “listen” to their conversations, track their activities across multiple pages, or steal their information.
- Data integrity—data cannot be modified or corrupted during transfer, intentionally or otherwise, without being detected.
- Authentication—proves that your users communicate with the intended website. It protects against man-in-the-middle attacks and builds user trust, which translates into other business benefits.
Not sure if your website has HTTPS?
Simply search your website like the following link example.
If your website can’t be viewed, it is not secured by HTTPS.
https://www.yourwebsite.com
What to do if your website isn’t secure?
You will need to install SSL Certificate to avoid any risks or warnings. If you don’t implement SSL Certificate, your visitors will see a “Not Secure” warning upon visiting your site.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is the standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between a web server and a browser. This link ensures that all data passed between the web server and browsers remain private and integral.
With SSL certificates, your visitors will see visuals like lock icon and green address bar that indicates well-trusted encryption is in use.
To setup an SSL Certificate for your website and avoid Google from telling visitors that your website is not secure, simply get in touch with your hosting provider and ask about their SSL Certificate and Verification process.
-Denver Dewar, RGD is an Associate Partner at 50 Carleton specializing in print production and website development, Denver has a combined expertise and passion for digital and physical products with an aim to create effective pieces of design and creative communications.
